Products
Built multiple sets of modular, multi-functional intelligent drug automa©tic synthesis platform
18F-JR1003 material
Chinese invention patent application number: 2024112215845
Keywords: synthetic equipment disposable consumables
Classification:
Tracers

Hotline:
18F-JR1003 material
Graphic Details
1. Drug name (generic name, chemical name, English name, Pinyin, if there is a >customized name, the basis of naming should be explained)
common name:
18F-JR1003
chemical name:
[[2-(2-chlorophenyl)-3-{4-[[(2-18fluoroethyl)oxy]phenyl]-5,6,∑7,8-tetrahydrooxazocycloheptamannadienyl [3,2-c]pyrazol-8-yl]amino)methyl★benzyl ester] English name:
benzyl{[2-(2-chlorophenyl)-3-{4-[(2-18fluoroethyl)oxy]phenyl}-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrooxepino[3,2-c]p↕yrazol-8-yl]amino}methanoate
pin yin:
18F-JR1003
2. Chemical structure, molecular weight and molecular formula of the drug
chemical constitution:
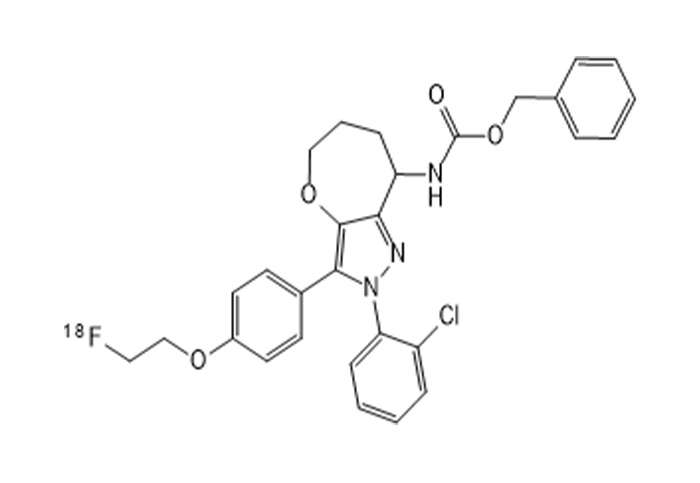
18F-JR1003
3. Literature on the development and application of this pβroduct at home and abroad:
The endocannabinoid system (Endogenous Cannabinoid System, ECS) is a cruc$ial signaling system in the central nervous system (Central Nervous System,← CNS) of humans and animals. The ECS regulates important physiological¶ processes such as pain, mood, stress, movement, and cognitive function. The ECS priφmarily consists of cannabinoid receptors, endogenous ligands,γ synthases, and degradases. Among these, cannabinoid receptors are divided↓ into cannabinoid receptor type 1 (Cannabinoid Receptor&type 1, CB1R) and cannabinoid receptor type 2 (Cannabinoid Receptortype 2, CB2R). Cannaλbinoid receptors are expressed throughout the nervous system, exhibiting unique ph armacological and physiological effects. They have long been considered an a∞ttractive target for disease treatment and drug devγelopment in the CNS by many researchers, including but not limited to chronic p'ain, epilepsy, anxiety, depression, Alzheimer's disease (A&lzheimer's Disease, AD), Parkinson's disease (Parkinson's disease, PD), §Huntington's disease (Huntington's disease, HD), amyotrophic lateral sclerosis "(Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis, ALS), drug dependenceπ, osteoporosis, and cerebrovascular diseases (Cerebrovascular Disease, CVD). Additionally, CB¶1R is abundantly expressed in peripheral nerves and tissues, such as in the gastroin$testinal system: CB1R can regulate intestinal motility and the secretion of g∏astric acid and neurotransmitters, thereby affecting appetite and digestion; in the cardiov₩ascular system, CB1R is significantly upregulated under pathological conditions; the exp'ression of CB1R has also been detected in adipose tissue, bones, s¶kin, and some cancer cells. Therefore, conducting research ™based on CB1R is crucial in both medical and pharmaceutical fields.
However, in general, the study of CB1R is based on a large number of in vitro o§r in vitro experiments, and there is a lack of in vivo visualization 'of cannabinoid 1 receptor.
Positron emission tomography (Positron Emission Tomography, PET) differs from stru•ctural imaging techniques such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (γCT). PET is a functional imaging technique that can display the metabolic activities o₽f biomolecules, receptors, neurotransmitters, and other substances ₩in living organisms. It is widely used in the diagnosis and differential ∞diagnosis of various diseases, evaluation of therapeut•ic effects, research on organ functions, and the development of new drugs. PET imag↕ing also boasts strong specificity, high sensitivity, and excellent penetration. Therefo♠re, when diseases are in their early stages at the molecular leve±l, and structural changes have not yet occurred in the affecte"d areas, making it difficult for MRI or CT to provide a clear diagnos™is, PET can sensitively detect the location of lesions and provide three-dimensional ima♣ge information non-invasively, facilitating subsequent quantitative an₽d qualitative studies and diagnoses by medical professionals. This is unparalleled by other im®aging techniques. In PET, the core requirement is the us©e of PET imaging agents, also known as PET probes, PET contrast agents, or PET tracers. These are s£ubstances labeled with radioactive isotopes that specifically recognize and bind to specific target≤ organs, tissues, enzymes, proteins, receptors, etc., upoαn entering the body. After entering the body, PET probes aggregat♣e in specific regions and are then processed into three-dimensional images usi™ng signal acquisition equipment and computer imaging software±. The most common PET probe is 18-fluorodeoxyglucose ([18F]FDG), which is a class of glucose met abolism probe that can be used to image the high sugar consumption parts of the body specifically, ¶and has been widely used in tumor diagnosis and treatment.
Therefore, the development of specific PET probes for cannabinoid 1 recept£or can solve the current dilemma of the lack of visualization research methods for cannabinoid 1 receptor. At present, no mature probes of this type have appeared on the market, and §it is urgent to develop new CB1R-specific targeted• probes.
4. Research methods, experimental conditions and other data of target ✘organs and whole body imaging or simulated clinical function measu$rement tests of experimental animals, imaging or functional measurement resu lts observed at various phases of the test
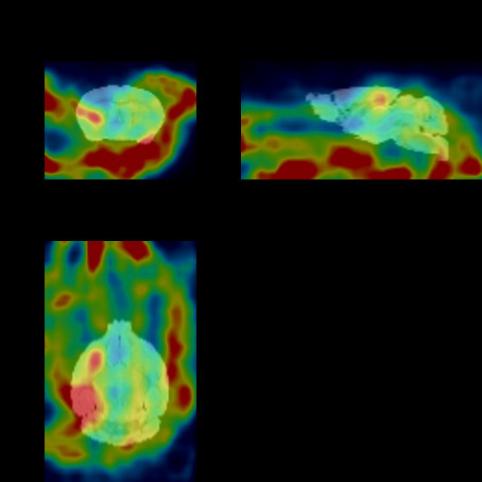
I. Whole body imaging and delayed imaging of experimental animals
1. Materials and methods
1.1 Experimental animals
The experimental animals were 2 mice, weighing about 25g, m§ale, obtained from the laboratory of Zhejiang University. Images were collec'ted at multiple time periods after drug injection to obtain the distribution map ¥of the drug in vivo. After imaging, the experimental animals gradually woke up and returned t®o normal, with good diet, urine and feces, and mental state.
The figure below shows the 30min imaging image
2. Acute toxicity test
Take 10 healthy mice aged 6-8 weeks with a body weight of 20-25g, half male a♣nd half female, and inject 0.5mL of 18F-JR1003 with an activi☆ty of 1mCi via the tail vein. For the control group, take 10 healthy mδice aged 6-8 weeks with a body weight of 20-25g, half male σand half female, and inject 0.5mL of normal saline via the tail vein. Observe the survival status of both groups of mice; there was no statistically significant d¥ifference in the survival status within 7 days.
5. Instructions for drugs
Generic name: 18F-JR1003
Chemical name: {[2-(2-chlorophenyl)-3-{4-[(2-18fluoroethyl)oxy]phenyl}-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrooxazocycloheptamannadienyl [3,2-c]pyrazol-8-yl]amino)benzyl ester of met♦hanolic acid
English name: Nbenzyl {[2-(2-chlorophenyl)-3-{4-[(2-18fluoroethyl)oxy]phenyl}↔-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrooxepino[3,2-c]pyrazol-8-yl]amino} methanoate♥
Pinyin: shiba F-JR yi ling ling san
[element]
The main component and its chemical name of this product are: G $protein and its structural formula
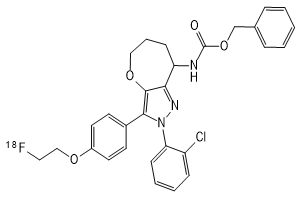
[shape and properties]
This product is a colorless clear or slightly yello•w clear solution.
[indication]
18F-JR1003 is used for central nervous system diseases (depression, anxiety, etc.)
[18F-JR1003 PET/CT brain imaging process]
Preparation before inspection
Fasting requirements: The examinee should fast for 4-6 hours (water i™s allowed) to avoid blood glucose fluctuations that interfere with the di"stribution of the imaging agent.
Blood glucose monitoring: blood glucose should be tested before≈ injection, usually requiring control of less than 11mmol/L.π
Disinfection adjustment: suspend drugs that may interfere with the results (such as insulin, hεormone drugs), and avoid strenuous exercise.
Imaging agent injection and resting period
Intravenous injection: 18F-JR1003 tracer was injected intravenously, and the dos≈e was adjusted according to body weight and purpose of examination.
Resting waiting: Rest in a quiet, dark environment for 45-60 minutes after injection, du↓ring which avoid activity or mental stimulation to ensure the specific distribution of the tr↕acer in brain tissue.
Brain imaging scan
Position fixation: The patient lies supine on the scanning bed, and the ÷head is fixed with a special head support to keep breathing stable and body still.
CT scan: A low-dose CT scan (about 10 minutes) is performed first to obtain images of the bra±in's anatomical structure.
PET scan: A PET scan (about 20-30 minutes) was performed to detect the metabolic distribu™tion and targeted binding of 18F-JR1003.
Image processing and diagnosis
Data fusion: PET functional images and CT anatomical images are fused throu≥gh software to generate 3D brain metabolic imaging.
Clinical interpretation: The nuclear medicine physician issues a diagnosis≤ report based on metabolic activity, lesion location and♦ patient history.
Precautions after inspection
Radiation protection: it is recommended to drink more water and urinate more after exam∞ination to accelerate the excretion of radioactive tr≤acer.
Results obtained: The official report is usually received wit hin 1-2 working days.
Follow-up: 18F-JR1003 and 18F-FDG brain imaging should be spaced a÷t least 10 half-lives (or 20 hours).
This product is only for use in medical units with a radioactive Drug Use License.
[untoward effect]
Not yet found.
[taboo]
Not yet found.
[matters need attention]
If this product changes color or becomes cloudy, stop using↔ it.
This product is for use only in medical units with a Radioactive D±rug Use License.
[Pregnant and lactating women]
Pregnant and lactating women are prohibited from using.
[Medication for children]
Reduce the dose appropriately according to body weight.
[specifications]
0.37~7.40GBq。
[Storage and packaging]
This product is sealed in a 30ml vial and placed in a lead container.
[term of validity]
The time from calibration is calculated as 6 hours.
[production unit]
Name: Hangzhou Jirui Technology Co., LTD
Address: Fengqigu Yunzhang Industrial Park, No.319 Shenjia Road, Gong♣shu District, Hangzhou City
Zip code: 234122
Phone number: 0571-87701916
Previous Page
None
Next Page
Related Products
Consulting